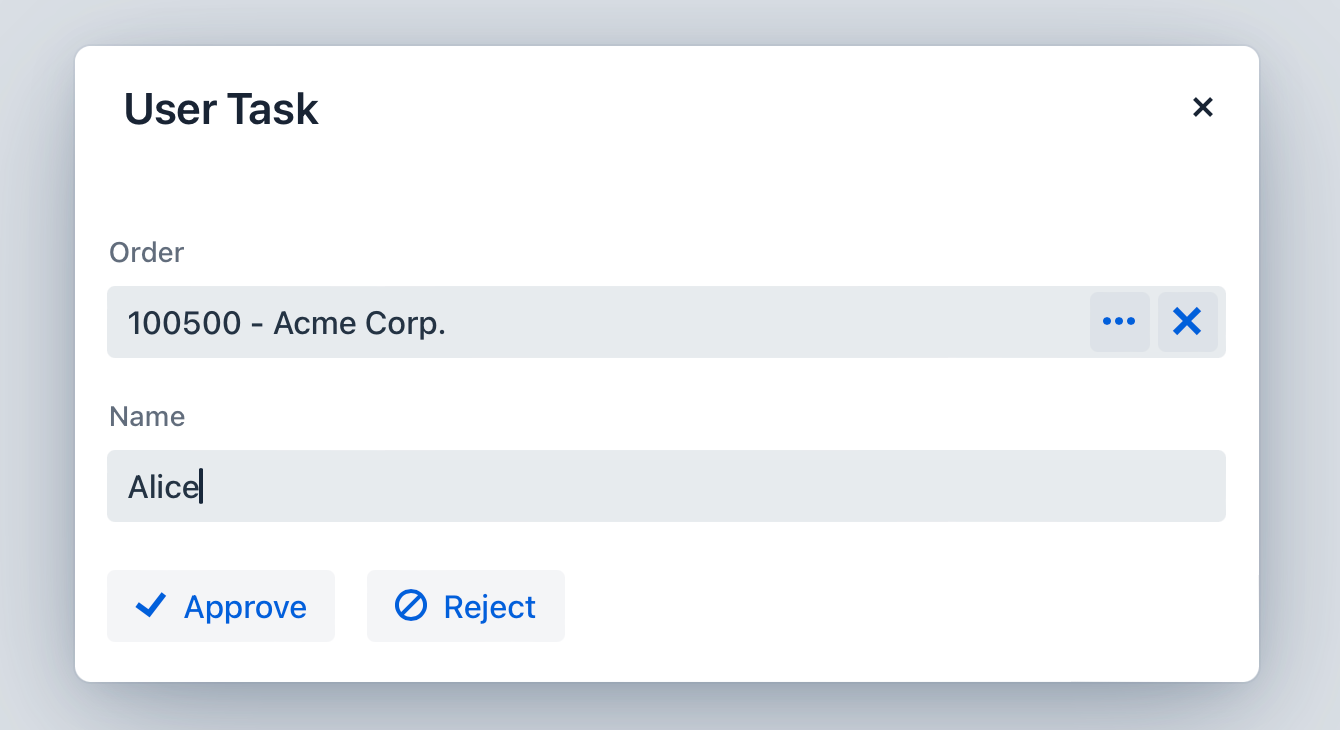
Input Dialog
Input dialog form это форма для ввода параметров для элементов Start Event или User Task. Диалог автоматически отображается когда пользователь запускает процесс или выполняет пользовательскую задачу.
Конфигурация
Чтобы настроить диалог, выберите элемент Start Event или User Task и установите для него тип Input dialog.
Form type
Эта настройка указывает тип процессной формы: No form, Input dialog, Jmix view, or Custom. Выбор типа отобразит соответствующие настройки.
Open mode
Настройка Open mode определяет, как отображается форма:
-
Dialog: форма отображается в диалоге.
-
Navigate: форма отображается как экран и будет доступна по собственному URL.
Input dialog parameters
Параметры связаны с полями ввода в диалоге. Чтобы добавить параметр, нажмите кнопку ![]() :
:
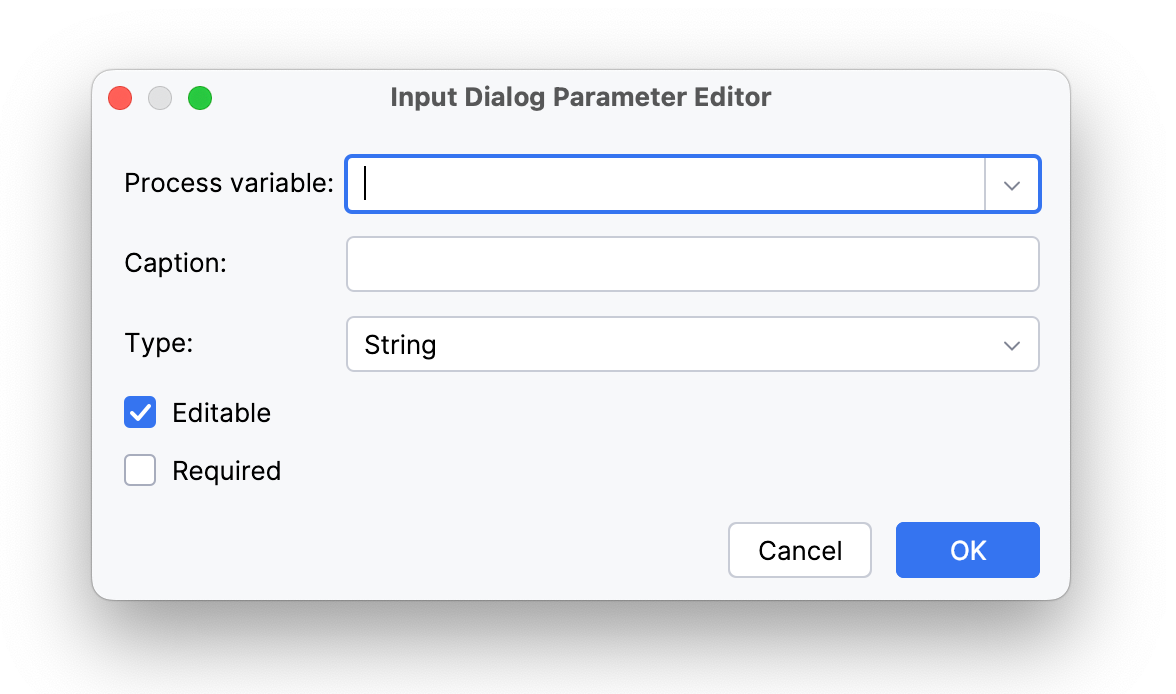
В редакторе выберите существующую переменную процесса или создайте новую, введя её имя. Затем добавьте заголовок и укажите тип параметра.
|
Параметры типов 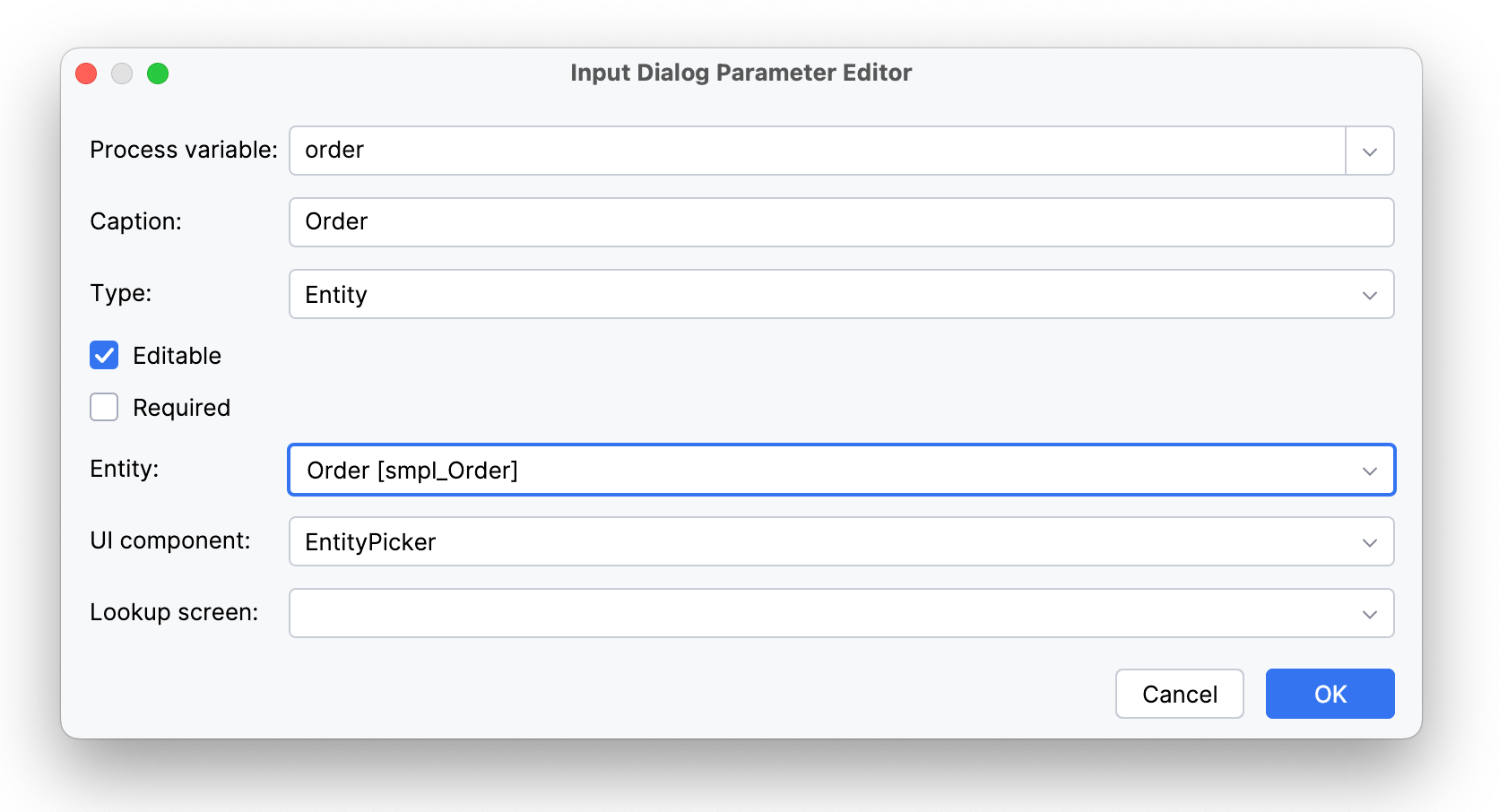
EntityPicker позволяет пользователям находить экземпляры через связанный экран. Если такой экран не указан, по умолчанию используется стандартный экран со списком экземпляров для этой сущности. ComboBox отображает экземпляры в выпадающем списке и требует JPQL-запрос для их загрузки. |
Business Key
| Эта настройка доступна только для Start Event. |
Укажите business key через один из четырех источников: переменная процесса, атрибут переменной сущности (e.g., ${entity.attribute}), вызов метода Spring bean или выражение Flowable.
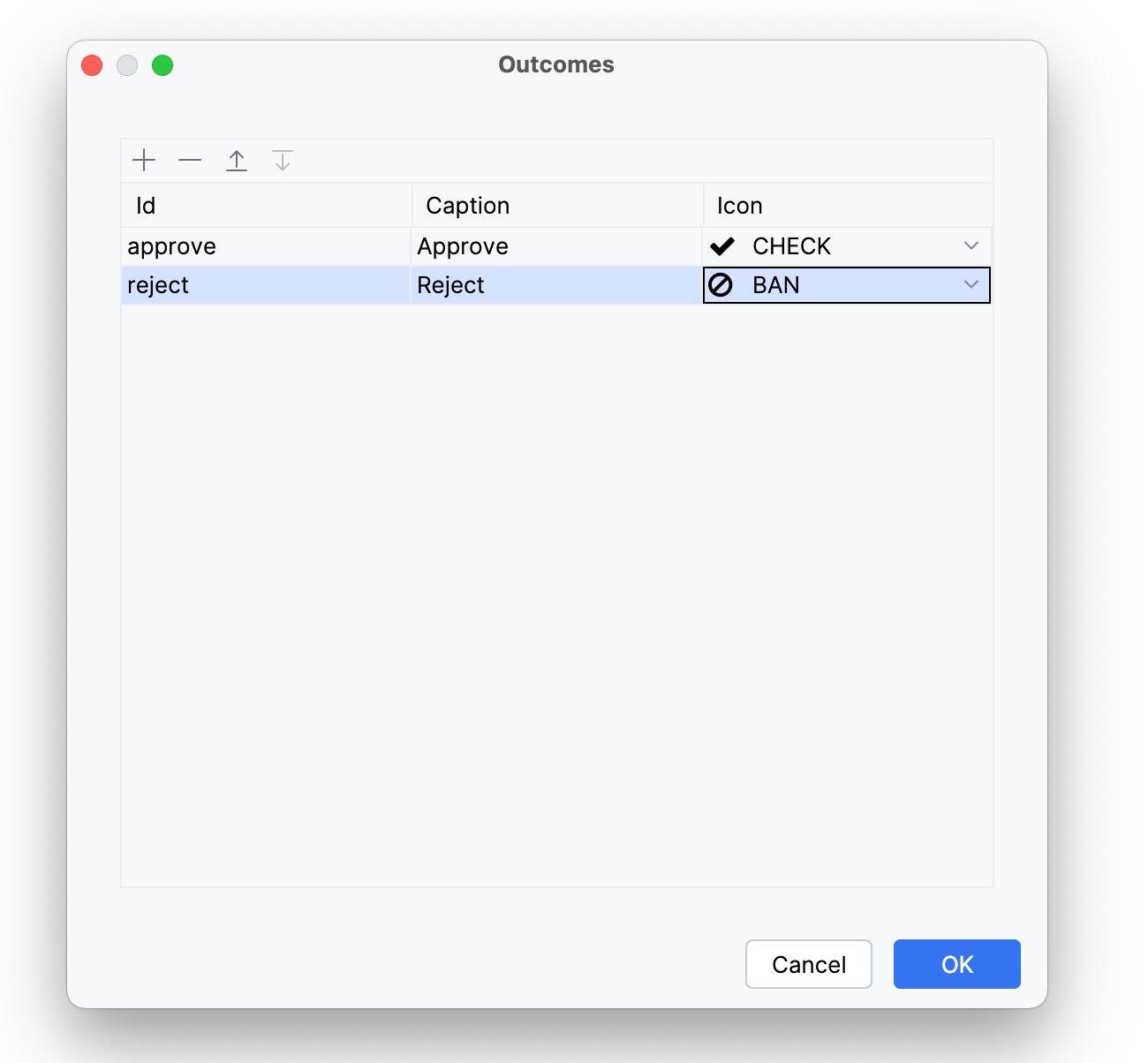
Outcomes
Результаты формы отмечают завершение пользовательской задачи, позволяя пользователям указывать её статус, например, утверждено или отклонено. Результаты отображаются как кнопки на процессной форме. По умолчанию, если вы не укажете ни один результат, используется стандартный результат Complete.
| Событие завершения задачи срабатывает независимо от конкретного результата. |
Чтобы добавить результат, нажмите кнопку ![]() . Затем используйте редактор, чтобы указать id результата, заголовок и иконку.
. Затем используйте редактор, чтобы указать id результата, заголовок и иконку.